Quick-Neuron™ GABAergic – Human iPSC-Derived Neurons (Healthy Donor)
Quick-Neuron™ GABAergic – Human iPSC-Derived Neurons (Healthy Donor)
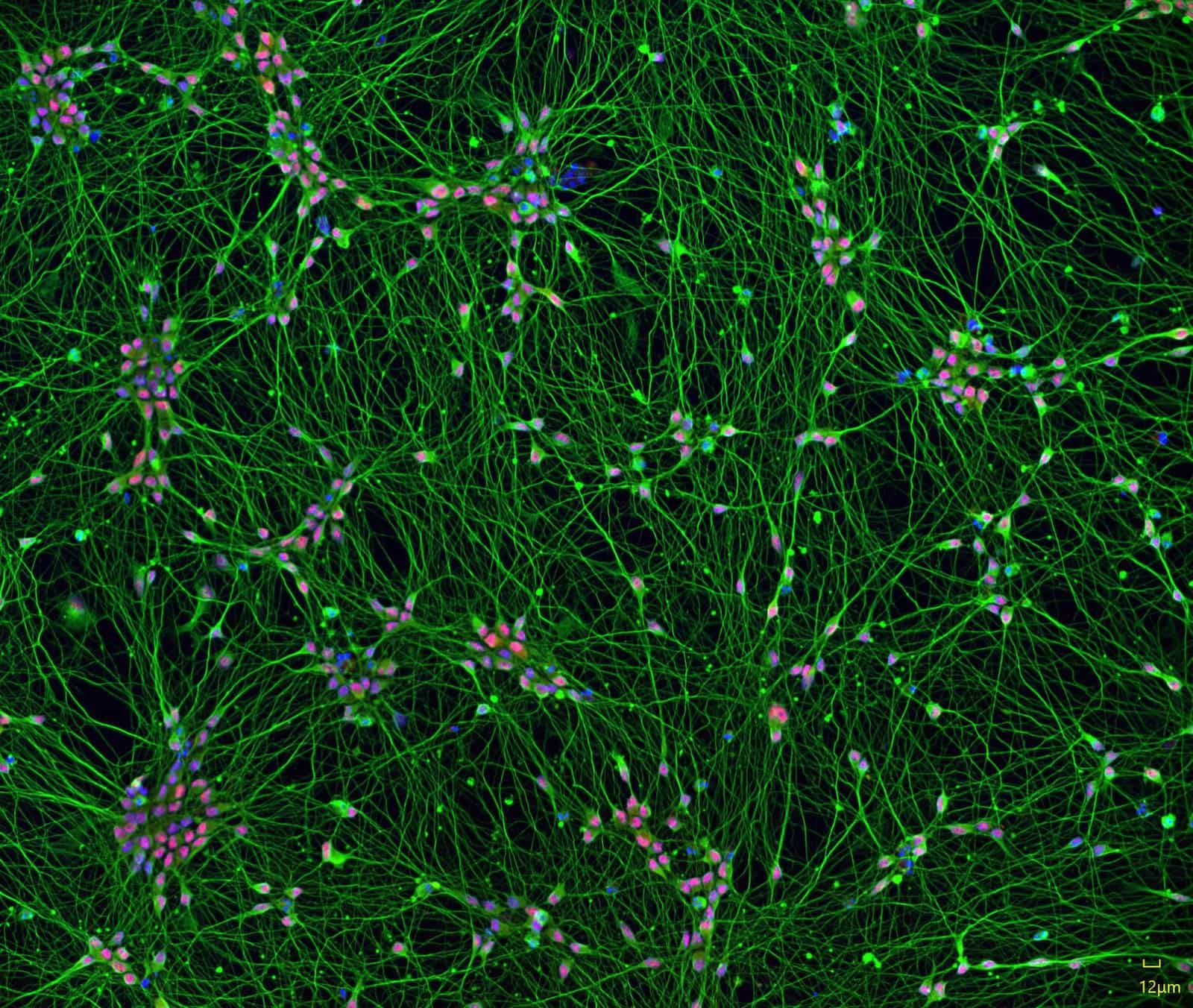
Our proprietary transcription factor-based stem cell differentiation method produces neurons without a genetic footprint. Quick-Neuron™ GABAergic – Human iPSC-derived Neurons display typical neurite outgrowth and express a variety of neuronal markers, such as the pan-neuronal marker TUBB3 (green), and the GABAergic subtype marker PVALB (red). When thawed and maintained according to the instructions in the user guide, the iPSC-derived neurons are viable long-term and are suitable for a variety of characterization and neurotoxicity assays.
$850.00
Advantages of iPSC-Derived GABAergic Neurons
~ 1 Week Differentiation
Functionally Validated
Highly Pure Population
No Genetic Footprint
GABAergic Neuron Protocol
Explore our detailed differentiation protocols, a step-by-step guide designed to simplify and optimize your laboratory procedures using our iPSC-derived cells and differentiation kits. These protocols leverage the latest advancements in iPSC technology to ensure efficient and reproducible results.


GABAergic neuron morphology is confirmed via phase contrast imagery: Representative phase contrast images of Quick-Neuron™ GABAergic – Human iPSC-derived Neurons on days 1-7 post-thaw (scale bar = 100 μm).
GABAergic Neuron Characterization
GABAergic Neuron Marker Expression

iPSC-derived GABAergic neurons express neuronal markers and display typical neurite growth. Immunofluorescent staining of Quick-Neuron™ GABAergic – mRNA Kit cell cultures shows typical neurite growth and expression of the pan-neuronal marker TUBB3 and the GABAergic neuron-specific marker PVALB on day 10 post-differentiation. Staining conditions: Anti-β-III tubulin monoclonal antibody (R&D Systems, Catalog Number: MAB1195, 1:250 dilution) in combination with a secondary antibody (Invitrogen,Catalog Number: A32723 Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, AlexaFluor Plus 488, 1:500 dilution). Anti-PVALB primary antibody (Novus Biologicals, Catalog Number: NB120-11427 , 1:1000 dilution) in combination with a secondary antibody (Invitrogen, Catalog Number: A11037 Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor 594, 1:500 dilution). Nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst 33342.

iPSC-derived GABAergic neurons express neuronal markers and display typical neurite growth. Immunofluorescent staining of Quick-Neuron™ GABAergic – mRNA Kit cell cultures shows typical neurite growth and expression of the pan-neuronal marker TUBB3 and the GABAergic neuron-specific marker GAD65/67 on day 11 post-differentiation (scale bar = 100 μm). Staining conditions: Anti-β-III tubulin monoclonal antibody (R&D Sys- tems, Catalog Number: MAB1195, 1:250 dilution) in combination with a secondary antibody (Invitrogen,Catalog Number: A32723 Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, AlexaFluor Plus 488, 1:500 dilution). Anti-GAD65/GAD67 primary antibody (Fisher Scientific, Catalog Number: PA5-36080, 1:400 dilution) in combination with a secondary antibody (Invitrogen, Catalog Number: A11037 Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Highly Cross-Adsorbed Sec- ondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor 594, 1:500 dilution). Nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst 33342.
Assessment of the GABA Expression Level of Quick-Neuron™ GABAergic Neuronal Culture

GABA expression level was determined by ELISA from Quick-Neuron™ GABAergic neuronal culture, using supernatants collected at day 14 and day 21 post differentiation (n=2). Data is expressed as the mean of 2 biological replicates ±SD. Supernatants of Quick-Neuron™ Excitatory neuronal culture at day 21 post differentiation were used as negative control.
Product Specifications
| Parameters | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Quick-Neuron™ GABAergic - Human iPSC-Derived Neurons |
| Catalog No. | GA-mRNA-HC-CW50065 |
| Product Components | Cryopreserved cells, Component N, Component P, Component G1, and Component G2 |
| Starting Material | iPSCs derived from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (CIRM line CW50065) |
| Storage Conditions | Frozen cells should be stored in liquid nitrogen (vapor phase). The rest of the components should be stored at -20°C. |
| Cell Type | GABAergic Neurons |
| Culture Type | Feeder Cell-Free |
| Disease | Healthy Donor |
| Donor Sex | Female |
| Donor Age At Sampling | 74 |
| Donor Race Ethnicity | Caucasian, not Latino |
| Patient History | See Resources section for more information. |
| Reprogramming Method | Episomal vector |
| Induction Method | Transcription factors delivered by synthetic mRNA |
| Growth Properties | Adherent |
| Number of viable cells | > 1.0 million viable cells per vial upon thawing |
| Cell viability and remaining live cells | >50% at day 1, >211 live cells per mm2 >50% at day 7, >211 live cells per mm2 |
| Differentiation | >80% TUBB3 positive cells >50% GAD65/GAD67 positive cells among TUBB3 positive cells |
| Sterility | No growth observed |
| Mycoplasma | No DNA detected |
| Morphological Observation | Cells are adherent and neurites exhibit substantial outgrowth, elongation and branching, indicative of a differentiated phenotype. |
| Restricted Use | For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
Resources
Quick-Neuron™ GABAergic – Human iPSC-Derived Neurons
Quick-Neuron™ GABAergic – mRNA Kit
Transcription Factor-Based Rapid Differentiation of Human iPSCs into Inhibitory, Excitatory and Sensory Neurons (Society for Neuroscience 2022)
Development of Electrophysiological Toxicity Assay System with iPSC-derived GABAergic Neurons Generated by a Rapid Differentiation Method (Safety Pharmacology Society 2023)
Establishment of High-Throughput Toxicity Assay System with iPSC-derived GABAergic Neurons Generated by a Rapid Differentiation Method (Safety Pharmacology Society 2023)
Related Products
FAQs
Does Quick-Tissue™ technology leave a genetic footprint?
Sendai virus (SeV) is an RNA virus, so it does not integrate into the genomic DNA. In principle, a foreign gene introduced intracellularly in the form of RNA is quickly translated and expressed because, unlike DNA, RNA does not need to enter the nucleus for forced expression, thereby providing no chance of mutagenesis. This is discussed in the following review paper: Yamamoto, et al., (2009) “Current prospects for mRNA gene delivery.” Eur. J. Pharm Biopharm 71, 484-489.
Will SeV remain active after differentiation?
No. The SeV used in our kits is a temperature-sensitive mutant that is active at 33℃ but becomes inactive at 37℃, which is the temperature instructed in the user guides post-differentiation.
Is Sendai virus (SeV) dangerous?
SeV is not pathogenic to humans (i.e., humans are not the natural host of the virus) and the infection does not persist in immunocompetent animals. Furthermore, SeV used in our kits does not produce infectious viral particles upon transduction to host hPSCs and is a temperature-sensitive mutant, such that it is active at 33℃ but becomes inactive at 37℃. However, because SeV can be transmitted by aerosol and contact with respiratory secretions and is highly contagious, appropriate care must be taken to prevent potential mucosal exposure to the virus. Our SeV-based kits must be used under Biosafety Level 2 (BL-2) containment with a biological safety cabinet or a laminar flow hood and with appropriate personal protective equipment. In the event that the virus comes into contact with skin or eyes, decontaminate the affected area by flushing with plenty of water and follow the safety manual prepared by your laboratory and approved by your Institutional Biosafety Committee.
Do I need a license agreement for any of Ricoh Biosciences’ products?
No. You don’t need any licence or material transfer agreement (MTA) to use our differentiation kits or iPSC-derived cells. However, please be advised that these products are for research use only.
What kind of transcription factors are used for differentiation induction?
It is a proprietary formulated RNA and cannot be disclosed.
Contact Us
Have a question about our products, services, or custom projects? Our team is here to help—reach out and we’ll get back to you as soon as possible.
Subscribe
By signing up you are agreeing to our Privacy Policy