Advancing Alzheimer’s Disease Research with iPSC-Based Panels
Advantages of Our Alzheimer’s Disease Panel
Comprehensive Data
RNA and whole-exome sequencing, including APOE status, and essential endpoint analyses.
Ready-to-Use
Pre-validated for immediate research use. No additional assay validation needed.
Biomarker Identification
Multi-omics data for precise patient stratification and targeted biomarker discovery.
Alzheimer’s Disease Panel Overview
Our Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) panel leverages precisely defined molecular data to facilitate the identification of biomarkers for patient stratification.

Quantify with Precision
Gain accurate and reliable quantitative data with our endpoint ELISA assays. Our AD Panel offers robust and reproducible ELISA data, enabling researchers to measure protein levels and detect changes in established biomarkers critical for AD research.

pTau, and Tau levels normalized per 1000 neurons assayed on week 6 post-differentiation in 10 AD patient-derived hiPSC excitatory neurons. Tau and pTau were measured in lysates by ELISA. Cell numbers were quantified with Hoechst by ICC. ApoE genotype is indicated for each hiPSC line: blue dots are for ApoE4/4, black dots are for ApoE3/4 and ochre dots are No ApoE4 (2/2 or 3/3).
pTau in Excitatory Neurons
Our Alzheimer’s Disease Panel provides valuable insights into patient-specific drug responses. Our healthy donor-derived excitatory neurons consistently respond to a GSK3β inhibitor, showing uniform sensitivity (see figure below). In contrast, AD patient-derived excitatory neurons exhibit high variability in drug response, mirroring the diversity seen in patients. This emphasizes the translational potential of our AD models, as they closely replicate the genetic and phenotypic diversity of the patient population. Such models are essential for identifying genetic determinants of drug resistance and improving patient stratification.
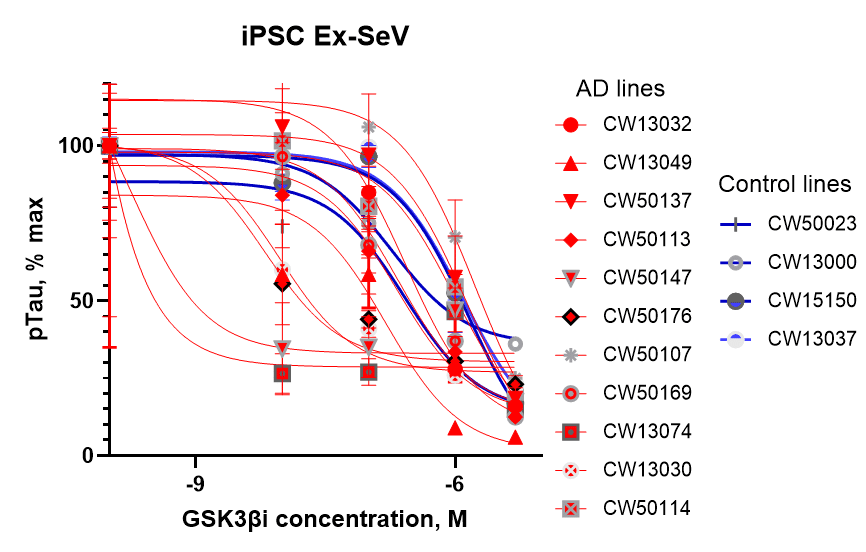
Excitatory neurons were differentiated from four healthy control subjects using our excitatory neuron Sendai virus kit. ELISA data indicates the levels of pTau (p-tau231; U/mL) protein in lysates, normalized to protein concentrations, at week 4 in culture. These neurons were treated with DMSO and various concentrations of GSK3βi (SAR502250), for 72 hours prior to sample collection.
Cohen’s D Analysis
Cohen’s D quantifies how effectively a drug differentiates patient populations based on gene variants. A high Cohen’s d indicates gene variants that play a critical role in differentiating patient subgroups, enabling informed decisions on drug efficacy and patient stratification.
Thresholds for interpretation:
- Small effect (𝑑=0.2: Minimal difference, limited relevance for stratification.
- Medium effect (𝑑=0.5): Moderate differentiation, potentially meaningful.
- Large effect (𝑑=0.8+): Strong differentiation, high importance for stratification.

Analysis of 183 variants across 29 Alzheimer’s disease (AD)-related genes. Variants were evaluated for their potential impact on drug efficacy and biomarker expression using Cohen’s d analysis. Variants with larger Cohen’s d values indicate stronger contributions to patient stratification and drug sensitivity differentiation.
Alzheimer’s Disease Panel Deliverables
| Parameter | Deliverable |
|---|---|
| Compounds Tested | 2 compounds |
| iPSC Lines | 11 AD patient-derived lines, 4 healthy donor lines |
| Readouts | Amyloid-β42 levels, Phosphorylated Tau (pTau) levels, Total Tau levels |
| Statistical Analysis | Cohen's d analysis is performed to evaluate biomarker data and determine the effect sizes |
| Project Timeline | ~8 weeks |
Alzheimer’s Disease Resources
Unlocking the Secrets of Alzheimer’s, Epilepsy, and More with Cutting-Edge iPSC Technology
Predicting Clinical Efficacy with Alzheimer’s Disease iPSC Panels
Patient-Derived iPSC Neuronal Models Reveal Alzheimer’s Disease-Associated Pathology and Provide a Platform for Drug Discovery (SfN 2025)
Contact Us
Have a question about our products, services, or custom projects? Our team is here to help—reach out and we’ll get back to you as soon as possible.
Subscribe
By signing up you are agreeing to our Privacy Policy